- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Wright SW Norris RL Mitchell TR. It is essential to differentiate between VOC-associated pain and chronic pain hyperalgesia neuropathy and neuropathic pain.
Using the Medicaid Analytic Extracts database the first SCD-related diagnosis claim index claim.
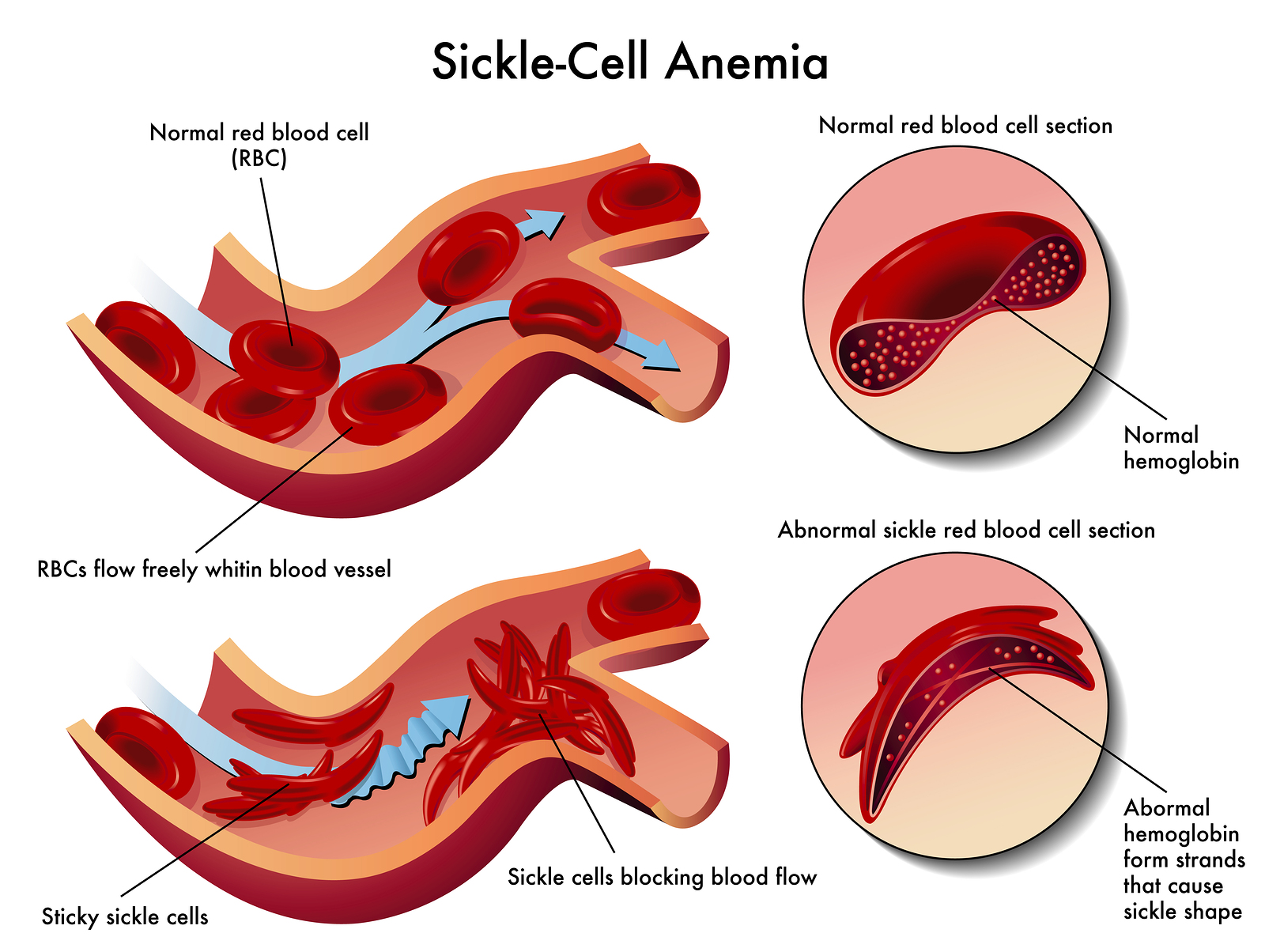
Vaso occlusive sickle cell crisis. May be associated with enlarged spleen as well see Acute splenic. Pain management in vaso-occlusive crisis is complex and requires multiple interventions such as pharmacologic nonpharmacologic and preventive therapeutic interventions. Epidemiologic data indicate that 52 percent of patients with sickle cell.
Vaso-occlusive crises caused by sickled red cells are responsible for chronic and acute damage to tissue and organs and cause recurrent and unpredictable episodes of acute pain often very violent in the affected parts of the body most usually the arms legs joints. Perlin E Finke H Castro O et al. Aplastic Vaso-occlusive Hemolytic and Sequestration 1.
The pathophysiology of VOCs. 2 In SCD COVID19 can potentially cause severe pulmonary complications either by directly causing severe pneumonia or by triggering a VOC andor ACS. Given the moderate-to-severe nature of the pain.
The study investigated the economic burden of vaso-occlusive crisis VOC among sickle cell disease SCD patients through assessment of overall utilization and costs and costs per VOC episode regarding the number of VOC episodes and health care setting respectively. A vaso-occlusive crisis most commonly involves the back. The stuck cells slow or even totally block blood flow.
Pharmacologic treatment involves the use of non-opioid and opioid analgesics and adjuvants - either singly or in combination - depending on the severity of pain. Approach to the Vaso-occlusive Crisis in Adults with Sickle Cell Disease Natural History of the Vaso-occlusive Crisis. Recurrent and unpredictable episodes of vaso-occlusion are the hallmark of sickle cell disease.
Intravenous fluids should be of sufficient quantity to correct. Early diagnosis treatment and prevention of a vaso-occlusive crisis VOC are critical to the management of patients with sickle cell disease. Vaso-occlusive episodes VOEs account for the majority of emergency department ED visits for children with sickle cell disease SCD.
The most common cause for hospitalization and the hallmark of sickle cell disease SCD is painful vaso-occlusive crisis VOC. Aplastic Crisis Sickle Cell Disease Background. Severe respiratory illness occurs in approximately 1520 of infected patients.
Types of sickle cell crisis. Am J Hematol 1994. Aplastic crisis is defined as an acute illness associated with haemoglobin below baseline for that patient associated with a substantially decreased reticulocyte count usually.
This can lead to acute hypoxia low oxygen levels as well as long term complications in the lungsThats when you have a sickle cell crisis. Ketorolac for sickle cell vaso-occlusive crisis pain in the emergency department. Enhancement of pain control with ketorolac tromethamine in patients with sickle cell vaso-occlusive crisis.
Sequestration crisis is the excessive pooling of blood in the liver and. Lack of a narcotic-sparing effect. Usually associated with acute infection including parvovirus.
Pain Patterns in the Vaso-occlusive Crisis. 1 As of March 31 2020 800049 laboratoryconfirmed cases and 38714 deaths have been documented globally. Vaso-occlusive crisis is treated with vigorous intravenous hydration and analgesics.
A vaso-occlusive crisis occurs due to the aggregation of sickled cells within a vessel. Symptomatic management and prevention of these events using the fetal hemoglobinreactivating agent hydroxyurea are currently the mainstay of treatment. A vaso-occlusive crisis or sickle cell crisis is a condition that occurs in people who have the disease known as sickle cell anemia.
Our current understanding of a vaso-occlusive crisis in patients with sickle cell disease SCD is that it is a multi-factorial process characterized by inflammation adhesion and multicellular aggregation of sickled red blood cells endothelial cells platelets and other blood cells result-ing in vaso-occlusion and acute severe pain. In sickle cell anemia there is a problem with the persons red blood cells which leads to them forming crescents that resemble the shape of a sickle rather than the normal rounded donut shape. Ann Emerg Med 1992.
Several studies including our own have documented a hypercoagulable state in patients with SCD which becomes further accentuated during pain crisis. We hypothesized that addressing key barriers to VOE care would improve receipt of analgesics and outcomes. The basic approach is to treat SCD pain symptomatically with escalating doses of non-opioid and opioid analgesics.
 Laboratory Evaluation Of Sickle Cell Disease In The Ed Taming The Sru
Laboratory Evaluation Of Sickle Cell Disease In The Ed Taming The Sru

 Sickle Cell Vaso Occlusive Crisis Sicklecell Crisis Grepmed
Sickle Cell Vaso Occlusive Crisis Sicklecell Crisis Grepmed
 Sickle Cell Disease Management And Complications With Sophie Lanzkron Md
Sickle Cell Disease Management And Complications With Sophie Lanzkron Md
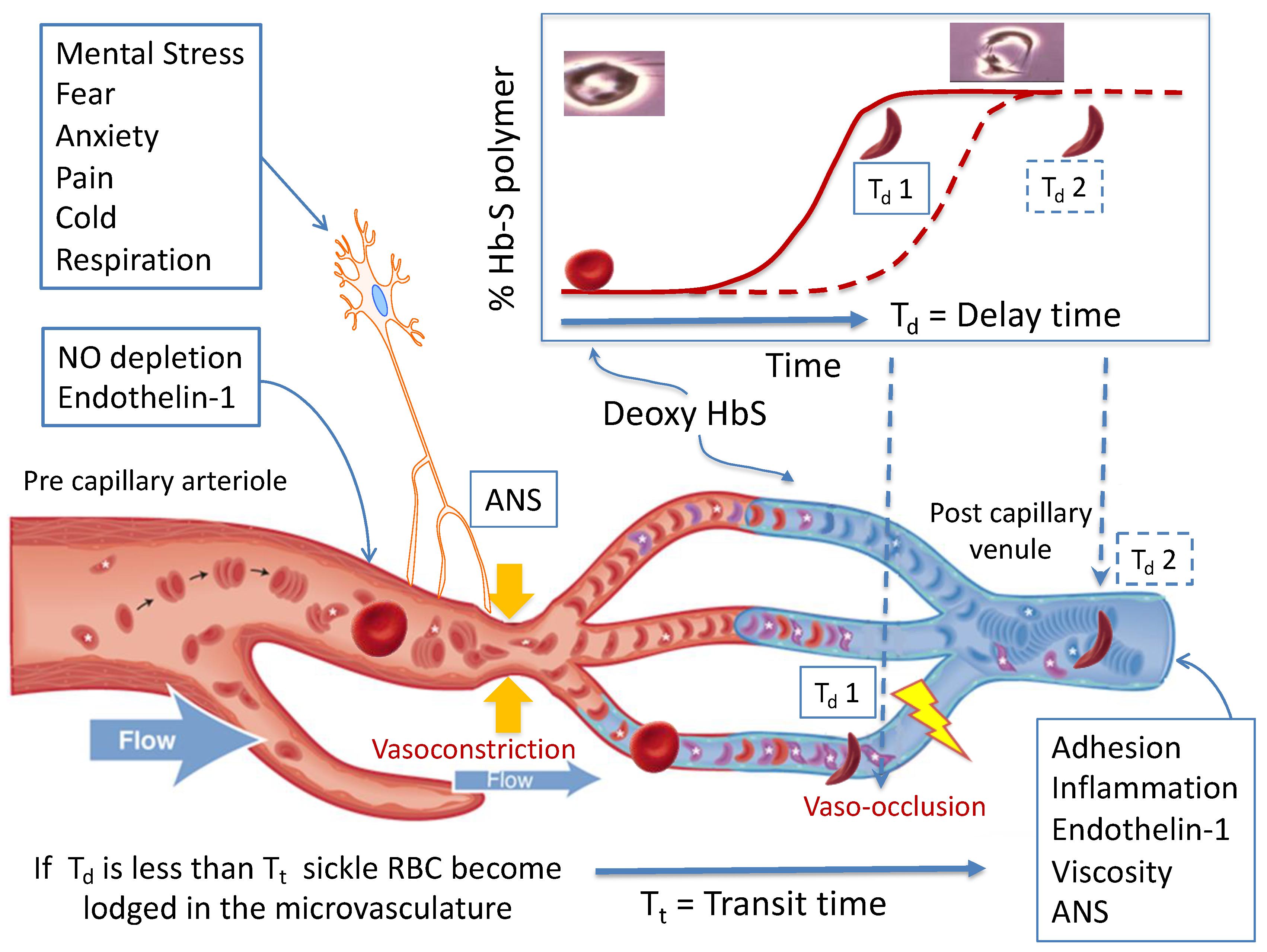 Jcm Free Full Text Vaso Occlusion In Sickle Cell Disease Is Autonomic Dysregulation Of The Microvasculature The Trigger Html
Jcm Free Full Text Vaso Occlusion In Sickle Cell Disease Is Autonomic Dysregulation Of The Microvasculature The Trigger Html
 Hypertension Medication Valsartan May Help Prevent Vaso Occlusive Episodes In Sickle Cell Disease Tif
Hypertension Medication Valsartan May Help Prevent Vaso Occlusive Episodes In Sickle Cell Disease Tif
 Vaso Occlusive Crisis In Sickle Cell Disease Current Paradigm On Pain Jpr
Vaso Occlusive Crisis In Sickle Cell Disease Current Paradigm On Pain Jpr
Pain Management In Vaso Occlusive Sickle Cell Crisis Emra
 Sickle Cell Disease A Practical Guide For Parents
Sickle Cell Disease A Practical Guide For Parents
 Efficacy And Safety Of Recently Approved Drugs For Sickle Cell Disease A Review Of Clinical Trials Experimental Hematology
Efficacy And Safety Of Recently Approved Drugs For Sickle Cell Disease A Review Of Clinical Trials Experimental Hematology
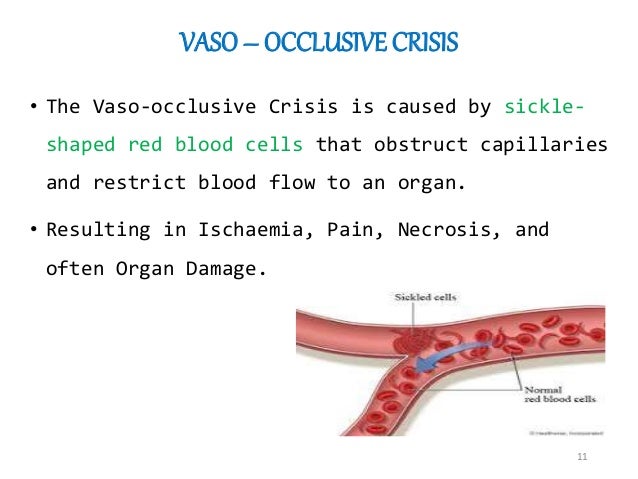 Prednisone Induced Vaso Occlusion
Prednisone Induced Vaso Occlusion
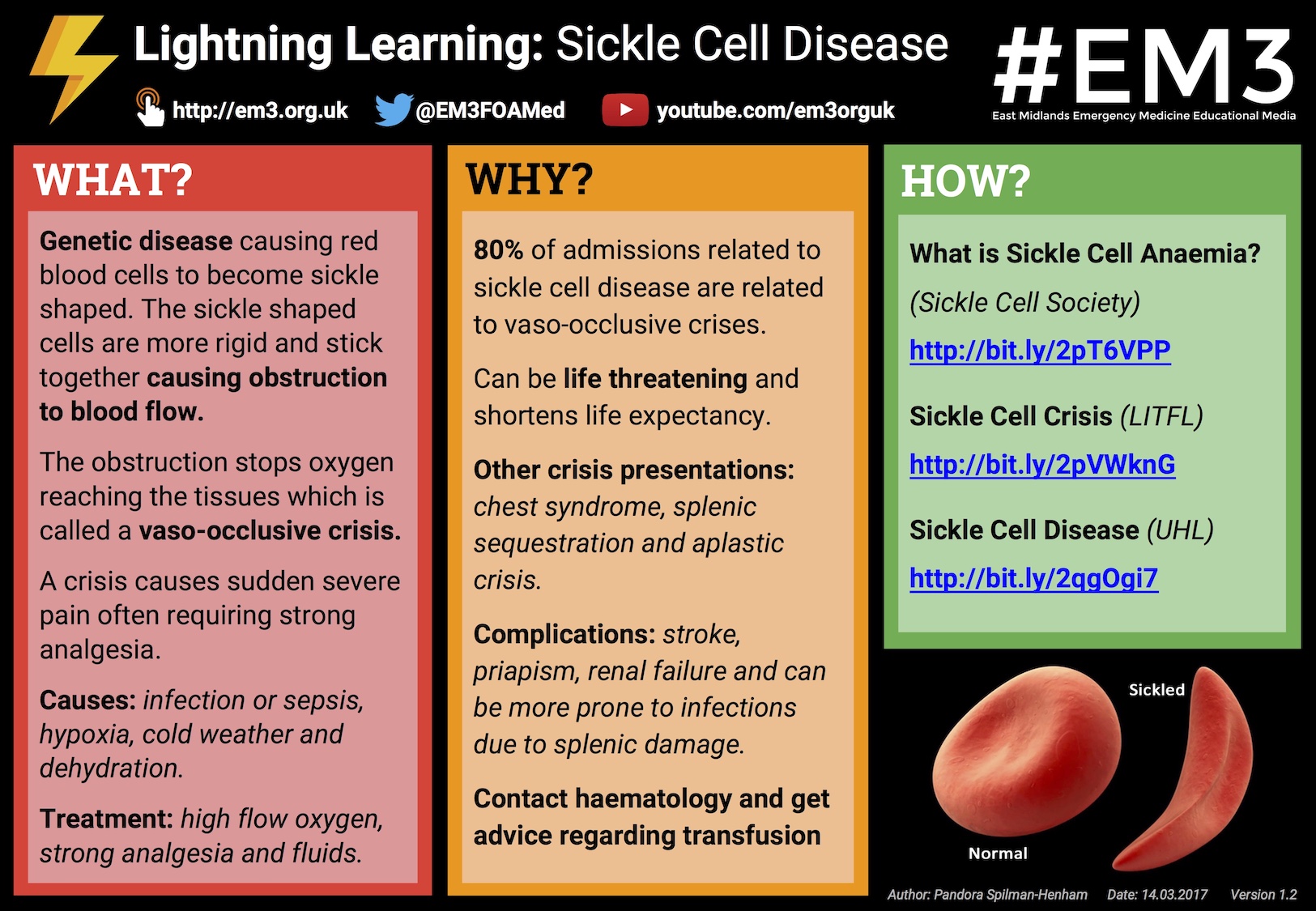 Lightning Learning Sickle Cell Disease Em3 East Midlands Emergency Medicine Educational Media
Lightning Learning Sickle Cell Disease Em3 East Midlands Emergency Medicine Educational Media
 Sickle Cell Anemia Nclex Review
Sickle Cell Anemia Nclex Review


Comments
Post a Comment